二进制搜索是一种在排序列表上有效工作的搜索技术。 因此,要使用二进制搜索技术来搜索某个列表中的元素,需要确保对列表是一个已排好顺序。
二进制搜索遵循分而治之的方法,其中,列表被分成两半,并且项目与列表的中间元素进行比较。 如果找到匹配,则返回中间元素的位置,否则根据匹配产生的结果搜索到两半中的任何一个。
二进制搜索算法如下。
BINARY_SEARCH(A, lower_bound, upper_bound, VAL)
第1步: [INITIALIZE] SET BEG = lower_bound
END = upper_bound, POS = - 1
第2步: Repeat Steps 3 and 4 while BEG <=END
第3步: SET MID = (BEG + END)/2
第4步: IF A[MID] = VAL
SET POS = MID
PRINT POS
转到第6步
ELSE IF A[MID] > VAL
SET END = MID - 1
ELSE
SET BEG = MID + 1
[END OF IF]
[END OF LOOP]
第5步: IF POS = -1
PRINT "VALUE IS NOT PRESENT IN THE ARRAY"
[END OF IF]
第6步: EXIT
复杂度
| 编号 | 性能 | 复杂性 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 最坏情况 | O(log n) |
| 2 | 最好情况 | O(1) |
| 3 | 平均情况 | O(log n) |
| 4 | 最坏情况空间复杂性 | O(1) |
示例
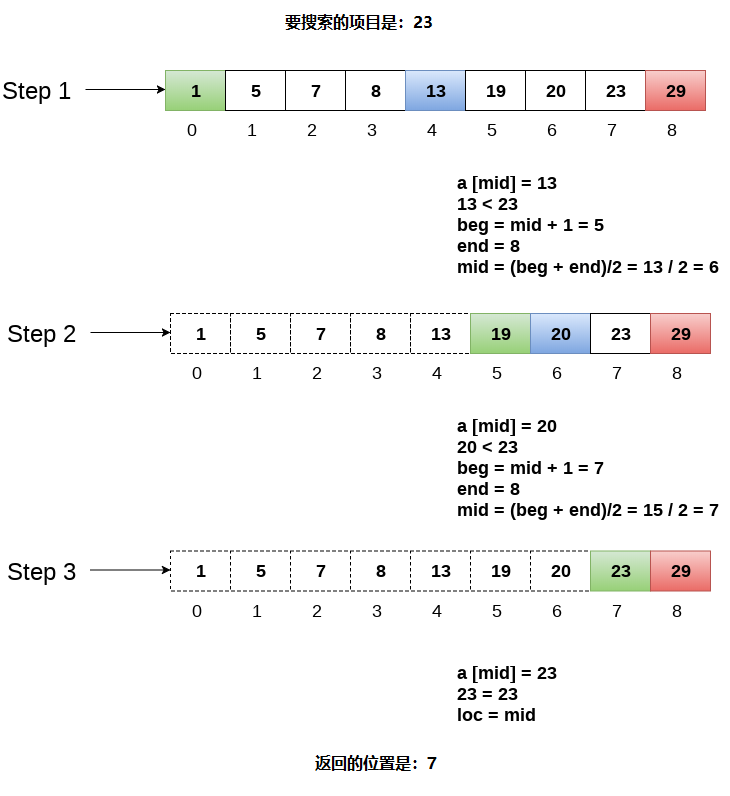
考虑有一个数组arr = {1,5,7,8,13,19,20,23,29},要在数组中查找项目:23的位置。
第1步:
BEG = 0
END = 8ron
MID = 4
a[mid] = a[4] = 13 < 23, 那么
第2步:
Beg = mid +1 = 5
End = 8
mid = 13/2 = 6
a[mid] = a[6] = 20 < 23, 那么;
第3步:
beg = mid + 1 = 7
End = 8
mid = 15/2 = 7
a[mid] = a[7]
a[7] = 23 = item;
那么, 设置 location = mid;
项目的位置为: 7
算法可参考以下图解 -
使用递归的二进制搜索程序
使用C语言实现 -
#include<stdio.h>
int binarySearch(int[], int, int, int);
void main ()
{
int arr[10] = {16, 19, 20, 23, 45, 56, 78, 90, 96, 100};
int item, location=-1;
printf("Enter the item which you want to search ");
scanf("%d",&item);
location = binarySearch(arr, 0, 9, item);
if(location != -1)
{
printf("Item found at location %d",location);
}
else
{
printf("Item not found");
}
}
int binarySearch(int a[], int beg, int end, int item)
{
int mid;
if(end >= beg)
{
mid = (beg + end)/2;
if(a[mid] == item)
{
return mid+1;
}
else if(a[mid] < item)
{
return binarySearch(a,mid+1,end,item);
}
else
{
return binarySearch(a,beg,mid-1,item);
}
}
return -1;
}
执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果:
Enter the item which you want to search
19
Item found at location 2
Java语言实现二进制查找 -
import java.util.*;
public class BinarySearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {16, 19, 20, 23, 45, 56, 78, 90, 96, 100};
int item, location = -1;
System.out.println("Enter the item which you want to search");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
item = sc.nextInt();
location = binarySearch(arr,0,9,item);
if(location != -1)
System.out.println("the location of the item is "+location);
else
System.out.println("Item not found");
}
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int beg, int end, int item)
{
int mid;
if(end >= beg)
{
mid = (beg + end)/2;
if(a[mid] == item)
{
return mid+1;
}
else if(a[mid] < item)
{
return binarySearch(a,mid+1,end,item);
}
else
{
return binarySearch(a,beg,mid-1,item);
}
}
return -1;
}
}
执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果 -
Enter the item which you want to search
45
the location of the item is 5
C#语言实现示例代码 -
using System;
public class LinearSearch
{
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = {16, 19, 20, 23, 45, 56, 78, 90, 96, 100};
int location=-1;
Console.WriteLine("Enter the item which you want to search ");
int item = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
location = binarySearch(arr, 0, 9, item);
if(location != -1)
{
Console.WriteLine("Item found at location "+ location);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Item not found");
}
}
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int beg, int end, int item)
{
int mid;
if(end >= beg)
{
mid = (beg + end)/2;
if(a[mid] == item)
{
return mid+1;
}
else if(a[mid] < item)
{
return binarySearch(a,mid+1,end,item);
}
else
{
return binarySearch(a,beg,mid-1,item);
}
}
return -1;
}
}
执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果 -
Enter the item which you want to search
20
Item found at location 3
Python语言实现代码 -
def binarySearch(arr,beg,end,item):
if end >= beg:
mid = int((beg+end)/2)
if arr[mid] == item :
return mid+1
elif arr[mid] < item :
return binarySearch(arr,mid+1,end,item)
else:
return binarySearch(arr,beg,mid-1,item)
return -1
arr=[16, 19, 20, 23, 45, 56, 78, 90, 96, 100];
item = int(input("Enter the item which you want to search ?"))
location = -1;
location = binarySearch(arr,0,9,item);
if location != -1:
print("Item found at location %d" %(location))
else:
print("Item not found")
执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果 -
Enter the item which you want to search ?
96
Item found at location 9
Enter the item which you want to search ?
101
Item not found
使用迭代的二进制搜索函数实现 -
int binarySearch(int a[], int beg, int end, int item)
{
int mid;
while(end >= beg)
{
mid = (beg + end)/2;
if(a[mid] == item)
{
return mid+1;
}
else if(a[mid] < item)
{
beg = mid + 1;
}
else
{
end = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
